Guest post by Jacqueline R. McAllister and Daniel Krcmaric
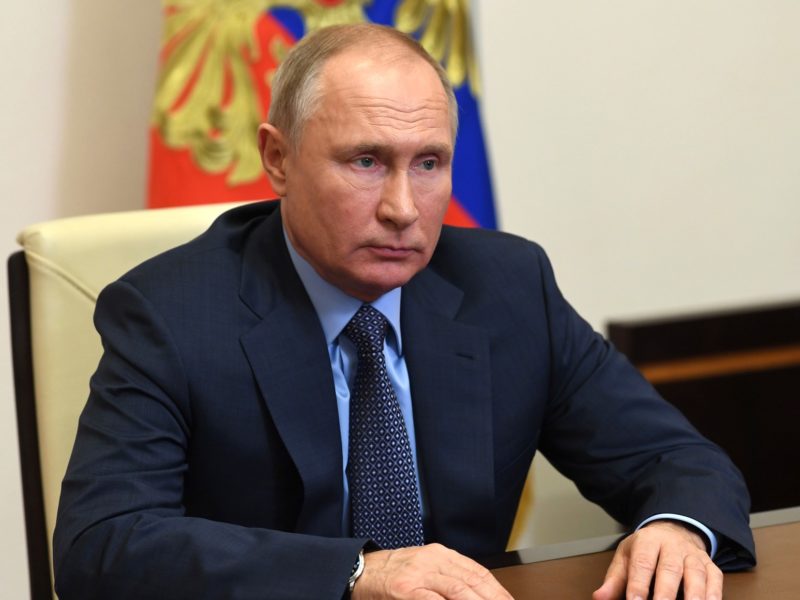
The International Criminal Court (ICC) shocked the world on March 17 by issuing arrest warrants for Russian President Vladimir Putin and his Commissioner for Children’s Rights, Maria Lvova-Belova. The ICC indicated it has reasonable grounds to believe that each bears criminal responsibility for unlawfully deporting and transferring children from occupied Ukraine to Russia—considered war crimes under international law. Rather than starting its ongoing investigation in Ukraine with arrest warrants for “small fry” war criminals, the ICC rolled the dice by going after its most prominent target ever: Vladimir Putin. Often considered the “most powerful man in the world,” Putin is the first leader with a permanent seat on the United Nations Security Council—and the first leader with an arsenal of nuclear weapons—to face an ICC arrest warrant.
What does all of this mean going forward? And how will the ICC arrest warrants influence the war in Ukraine?
It is important to start by managing expectations: Neither Putin nor Lvova-Belova is likely to land in the ICC’s dock anytime soon. Since the ICC does not have a police force, it relies on state cooperation for enforcement. Russia refuses to recognize the ICC, and it is inconceivable that Putin and Lvova-Belova will voluntarily turn themselves into the court. The road ahead for securing justice will be bumpy.
Nonetheless, the ICC’s arrest warrants may have several implications for the war, some negative, some positive.
In terms of negative implications, the ICC arrest warrants are unlikely to deter Russian forces from continuing to commit atrocities in Ukraine. In fact, they may perversely convince Russians to double down on their atrocity crimes. This may already be happening in Ukraine. During his surprise visit to Russian-occupied Mariupol after the warrants were announced, Putin thumbed his nose at the ICC by visiting a children’s center. Other Russian authorities have responded to the ICC arrest warrants by signaling that “more deportations are on the way.” Ukrainian civilians—the very people who have already borne the brunt of the war—may continue to suffer as their children are abducted and put on display in Red Square photo-ops and at concerts celebrating the war.
The ICC arrest warrants are also likely to make it harder for Ukraine and its Western allies to reach a negotiated settlement with Russia. The logistics of negotiating peace are more complex now that Putin is in the ICC’s sights. Will leaders in Western democracies be willing to negotiate directly with an accused war criminal? Might they insist that Putin be removed—as they did for other brutal leaders—as a precondition for meaningful negotiations? Will Putin be willing to travel abroad for a prospective peace conference? The ICC’s 123 member states now have a legal obligation to arrest him if he ever sets foot on their territory, making them undesirable sites for a peace conference. It is possible that China, fresh off its role in brokering a deal between Iran and Saudi Arabia, could play host. But China’s actions thus far have convinced Western officials that it would not be a neutral broker in Ukraine.
There are some positive implications, however. The arrest warrants could facilitate efforts to hold Putin and other top leaders criminally accountable. For example, following Serbian leader Slobodan Milošević’s indictment at the Yugoslav Tribunal, several of his key associates began sharing a wealth of much-needed evidence. As Yugoslav Tribunal Deputy Prosecutor Graham Blewitt explained in an interview with one of the authors, “Milošević opened up other areas of interest. Once he was indicted for Kosovo, we could then bring indictments for Bosnia and Croatia, because people talked to us. Some people were trying to do the right thing, and some people wanted to do deals.” In conjunction with military intelligence from Western governments, such testimony and documents linking top leaders to crimes proved crucial for prosecuting those who were previously beyond the Yugoslav Tribunal’s reach. It is possible that some in Putin’s inner circle could end up doing the same for the ICC.
If history is any indication, the ICC’s arrest warrants may also shore up support for Ukraine’s war effort, particularly from NATO. During the Kosovo War, the Yugoslav Tribunal’s indictment of Milošević helped to solidify support for NATO’s Operation Allied Force in Kosovo. Specifically, as NATO’s air campaign ground on with seemingly no end in sight, pressure mounted in Western capitals to bring hostilities to a close. In the face of such pressure, keeping the Alliance together posed a real challenge. The Milošević indictment, according to NATO Supreme Allied Commander Wesley Clark, was “a huge win. Nothing was more likely to stiffen the Allies’ resolve and push us forward into a winning situation than this indictment.”
Since Russia’s invasion of Ukraine over a year ago, questions have persisted about whether NATO, the US, and European Union will sustain their crucial support for Ukraine’s war effort over the long haul. Indeed, Putin seems to be gambling that Ukraine’s supporters will eventually falter in their commitment to its cause. If NATO’s experience in Kosovo is any indication, the ICC’s arrest warrants might help Ukraine’s backers to keep calling Putin’s bluff.
Jacqueline R. McAllister is an Associate Professor of Political Science at Kenyon College and will join the State Department’s Office of Global Criminal Justice in 2023 as a Council on Foreign Relations fellow. Her research appears in leading scholarly and foreign affairs magazines. Daniel Krcmaric is an Associate Professor of Political Science at Northwestern University and the author of The Justice Dilemma: Leaders and Exile in an Era of Accountability. He is currently writing a book about the turbulent relationship between the United States and the International Criminal Court.







1 comment
Where was the International Criminal Court when Obomber destroyed Libya? When the Bushes made wars of aggression against Iraq? When NATO bombed civilians in Yugoslavia? When Bush invaded Afghanistan? When U.S. officers repeatedly commit the very crime for which we hanged the NAZI high command at Nuremburg, the ICC looks the other way. Where was the ICC when Israel bombed Gaza, killing thousands of civilians, including children? Follow the money. The hypocrisy of the ICC is beneath contempt!