By Timothy Sisk
The row between International Olympic Committee (IOC) President Thomas Bach and Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky over potential Russian and Belarussian athlete participation at Paris 2024 exposes the Achilles’ Heel of the Olympic Games: the peace-promising celebrations are inescapably ensnared in nation-state power politics.
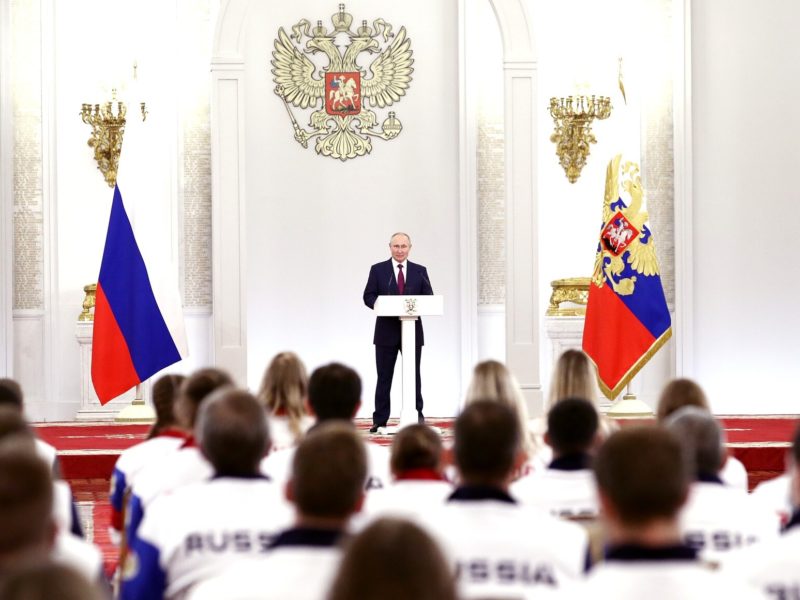
The IOC announced on January 25 a proposal to facilitate participation in the 2024 Olympic Games for individual athletes from Russia (and close ally Belarus) individually and neutrally in the Paris games. The statement reversed an IOC Executive Board decision from February 28, 2022, to impose more sweeping participation sanctions on Russia following the Ukraine invasion.
The International Paralympic Committee announced on January 23 that it would “follow” the IOC decision for the paralympic events, with President Andrew Parsons noting that “We wish to reiterate that we hope and pray that the conflict comes to an end, that no more lives are taken, and that we can run sports and politics separately.” Parsons gave a rousing denunciation of the Ukraine invasion from the podium in his opening-ceremonies speech as the Russian tanks rolled toward Kyiv, demanding “dialogue and diplomacy, not war and hate.”
The potential of Russian athletes participating at the 2024 Olympic and Paralympic Games in Paris while the horrors and war crimes unleashed by Russia in Ukraine and documented by a United Nations independent commission continue to unfold would constitute, Zelensky said, “a manifestation of violence.” Addressing a February 10 meeting of 35 foreign ministers convened to consider a boycott if Russians were to appear in the Olympic arena, he said, “If the Olympic sports were killings and missile strikes, then you know which national team would occupy the first place.” Reversing her earlier stance, Paris Mayor Anne Hidalgo said she supports Zelensky’s call and journeyed to Kyiv on February 9 in solidarity.
Olympic powerhouses including the US, UK, Germany, Australia, and New Zealand together with Nordic and Baltic states are drawing a line in the beach-volleyball sand against Russian and Belarussian participation at Paris. Some want to allow for a “dissident team” from these countries to be formed.
In a slope-side appearance at the World Alpine Skiing Championships in Courchevel on February 12, Bach defended the IOC’s position: “No, history will show who is doing more for peace.”
The IOC’s approach to addressing the thorny question of Russian participation in the 2024 Games is similar to the sporting world’s response to the sprawling Russian state-sponsored doping scandal and cover-up when it hosted the 2014 winter games in Sochi. In December 2019, the World Anti-Doping Agency slapped a set of four-year sanctions on Russia, including banning Russian teams from Olympic-related events, barring use of its flag and anthem, and imposing diplomatic and other sanctions. Athletes could participate but could not represent Russia as such, but rather the Russian Olympic Committee (ROC).
No worries for Russia, however, as the ROC and individual athletes easily evaded the athlete-representation sanctions. The uniforms of the Russian athletes at the Beijing 2022 Winter Games were fashion-forward, black splashed with the colors of the Russian flag. Nancy Armour writes in USA Today Sports that in Tokyo 2020 (which happened in 2021, delayed by the pandemic), 45 of the Russians’ 71 medals were won by members of the Russian Army’s Central Sports Club, according to the Ukrainian foreign ministry. Russian gymnast Ivan Kuliak was slapped by the International Gymnastics Union with a year-long ban for “shocking behavior” for sporting on his chest the invasion-related “Z” symbol on the podium standing next to a Ukrainian athlete (Kuliak won bronze; the Ukrainian, Illia Kovtun, won gold).
Despite rules against political speech, athletes are increasingly turning to tattoos, nail polish, hairstyles, and other clever non-verbal ways to communicate patriotism while staying just inside the non-political appearance rules of the IOC and the sport federations. Symbols are amorphous and consistently changing, so the IOC wages a Sisyphean struggle to contain political speech within the Olympic arena. In the run-up to Tokyo 2020, following the recommendations of the IOC’s Athletes Commission, the Executive Board reformulated its Rule 50.2 code on athlete political speech to allow more personal political speech outside its venues, ostensibly to prevent future “Black Power”-type salutes from the podium as courageously seen in the 1968 Mexico City games.
The IOC appears to see national de-identification as a way to cope with its Achilles’ Heel vulnerability to power politics. It touts the idea of a modern-day Olympic Truce similar to that found in the ancient Greek Olympics, on which the modern spectacle is at best loosely based; the truce allowed athletes to travel to the festivals unimpeded.
The IOC and sport federation bodies need the Russia participation question to be resolved soon, as qualifying events for Paris 2024 are in motion around the world. But the row continues. The Olympic Council of Asia has apparently invited Russian and Belarussian gymnastics and wrestling athletes to qualify through its auspices, while two United Nations special rapporteurs have backed the IOC approach on the basis of athlete human rights.
Russia’s February 2022 invasion rendered any Olympic truce a scrap of paper. The Kremlin unleashed the deadly operation on Kyiv just days before the Opening Ceremonies of the 2022 Beijing Paralympic Winter Games. In the year since, a reported 228 Ukrainian athletes and coaches have been killed.
In waging war while the Olympic flame burns, Russia is a serial offender: its military invaded Georgia in the period between the 2008 Olympic and paralympic events, and then seized the Crimean peninsula in 2014, in a similar window between these events.
The close association of the Olympic Games with the power politics of nation-states may well explain why the IOC, its president, nor any global sports body or figure have been awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in its 121-year history roughly commensurate with the Olympics. (The Prize was won by an Olympic medalist in 1959—UK diplomat Philip Noel-Baker—but not for his Olympic achievement; the Norwegian Nobel Committee cited his disarmament efforts).
The power-politics Achilles’ Heel of the Olympics disables its potential for furthering international peace. For how sport might contribute to peace, one must look elsewhere in youth-based development and peacebuilding programs, in the public good work of celebrity and everyday athletes, coaches, and humanitarian organizations, or in the Olympic Refugee Team which debuted in Rio 2016 that allows athletes displaced abroad to participate.
Beyond the Olympic Refugee Team, it is time for any athlete as an individual to have a path to qualifying for the Olympic Games with no broader representation of national identity beyond legal citizenship. Such a step might begin to free the Olympics from its disabling ensnarement in the power politics of nation-states and begin to give meaning to the right of individuals to participate in global sport outside of truce-destroying nation-states.